Did you know that 1 in 10 Babies Born Prematurely, facing significant challenges right from the start? Picture this: out of every ten newborns you see, one arrived ahead of schedule. Premature birth isn’t just an early entrance into the world; it’s a critical issue affecting the health and survival of these tiny infants. From struggling to breathe to battling infections, premature babies often face a rocky start to life. In this article, we’ll delve into the impacts of premature birth, shedding light on the hurdles these little ones and their families must overcome.

Introduction:
Premature birth, defined as birth before 37 weeks of pregnancy, is a significant global health issue affecting approximately 1 in 10 babies worldwide. This guide aims to shed light on the complexities surrounding premature births, including their health, economic, and social impacts, as well as initiatives to raise awareness and support premature babies and their families.
Understanding Premature Births:
Premature birth can occur due to various factors, including maternal health conditions, lifestyle choices, infections, and environmental factors. Understanding the causes and risk factors is crucial in addressing and preventing premature births.
Health Impacts of Premature Births:
Premature babies often face numerous health challenges, including respiratory problems, developmental delays, and long-term disabilities. Premature birth can also increase the risk of infant mortality and other health complications throughout the child’s life.
Economic and Social Impacts:
Premature birth imposes significant economic burdens on families and healthcare systems due to increased medical expenses and long-term care needs. Moreover, it can disrupt family dynamics and lead to emotional stress for parents and caregivers.
Global Initiatives and Awareness Efforts:
Numerous organizations and initiatives are working to raise awareness about premature birth and provide support to affected families. These efforts aim to improve access to healthcare, promote prenatal education, and advocate for policies that prioritize maternal and infant health.
Addressing the Causes of Premature Births:
Efforts to address the root causes of premature birth involve improving maternal healthcare, reducing exposure to risk factors, and promoting healthy lifestyle choices during pregnancy.
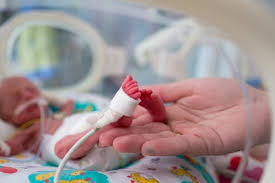
Prenatal care, education, and early intervention play crucial roles in preventing premature births.
Supporting Premature Babies and Families:
Support services for premature babies and their families include neonatal intensive care, developmental therapies, and emotional support programs. Creating a supportive environment can enhance the well-being of both the baby and the family.
Preventive Measures and Best Practices:
Preventive measures such as regular prenatal care, avoiding harmful substances, and managing chronic health conditions can help reduce the risk of premature birth. Best practices include promoting maternal nutrition, breastfeeding, and maternal mental health support.
Cultural and Societal Perspectives:
Cultural beliefs and societal norms can influence perceptions of pregnancy, childbirth, and premature birth. Understanding cultural perspectives is essential for providing culturally sensitive care and support to diverse populations.
Overcoming Barriers to Care:
Barriers to accessing healthcare, including financial constraints, lack of education, and geographical remoteness, can exacerbate the challenges faced by premature babies and their families. Efforts to overcome these barriers involve improving healthcare infrastructure, expanding insurance coverage, and increasing community outreach.
Research Breakthroughs and Innovations:
Ongoing research aims to advance our understanding of premature birth and develop innovative interventions to improve outcomes for premature babies. Breakthroughs in medical technology, genetic research, and public health strategies hold promise for reducing the prevalence and impact of premature birth.
Future Outlook and Challenges:
While progress has been made in addressing premature birth, significant challenges remain, including disparities in access to care, rising healthcare costs, and emerging health threats. Continued collaboration and investment are needed to ensure better outcomes for premature babies and their families.
Conclusion:
Premature birth is a complex global health issue with far-reaching impacts on health, survival, and well-being. By understanding the causes, impacts, and preventive measures associated with premature birth, we can work towards reducing its prevalence and improving outcomes for premature babies and their families worldwide.

FAQS:
Q1:What is the survival rate of premature babies?
The survival rate of premature babies can vary depending on various factors such as gestational age, birth weight, and access to medical care. Generally, advancements in neonatal medicine have improved survival rates for premature infants, with many surviving and thriving with proper medical intervention.
Q2:What percentage of babies come early?
The percentage of babies born prematurely, or preterm, varies across different populations and regions. In some areas, around 10% of babies are born prematurely, while in others, the rate may be higher or lower.
Q3:What is the worldwide incidence of preterm birth?
The worldwide incidence of preterm birth is approximately 10%, according to estimates by the World Health Organization (WHO). This means that about 1 in 10 babies worldwide is born prematurely.
Q4:What percentage of babies are born prematurely?
The percentage of babies born prematurely varies depending on the region and other factors, but globally, approximately 10% of babies are born prematurely. This means they are delivered before 37 weeks of gestation. However, it’s important to note that this figure can fluctuate and may be higher in certain populations or regions. Premature birth can pose various health risks for the baby and may require specialized medical care.


